What is H2 and Why Uruguay?
What is Hydrogen and what is it used for today?
Hydrogen is the first element on the periodic table. It is the lightest chemical element, its atom contains a proton and electron, and is stable in the form of a diatomic molecule (H₂).
In our planet it is unusual to find the diatomic molecule H₂ freely, also called Hydrogen. It is most common to find the Hydrogen as part of compounds, because it reacts with many chemical elements to form: water, salts, hydrides, acids, methane, ammonia, polymers, etc.
Currently 99% of H₂ is produced from fossil fuels (mainly from Natural Gas and Coal) and therefore greenhouse emissions are generated in the process.
At present, more than 120 million tons of Hydrogen are produced per year, of which two thirds are in the form of pure H₂ and one third are in mixtures with other gases. The demand is concentrated in the use in refineries, ammonia production (to obtain fertilizers and other products), and indirectly for the production of methanol, steel and others.
What is Green Hydrogen?
Green Hydrogen is that which is produced without the participation of fossil fuels. The production of Green Hydrogen is carried out solely from renewable energies.
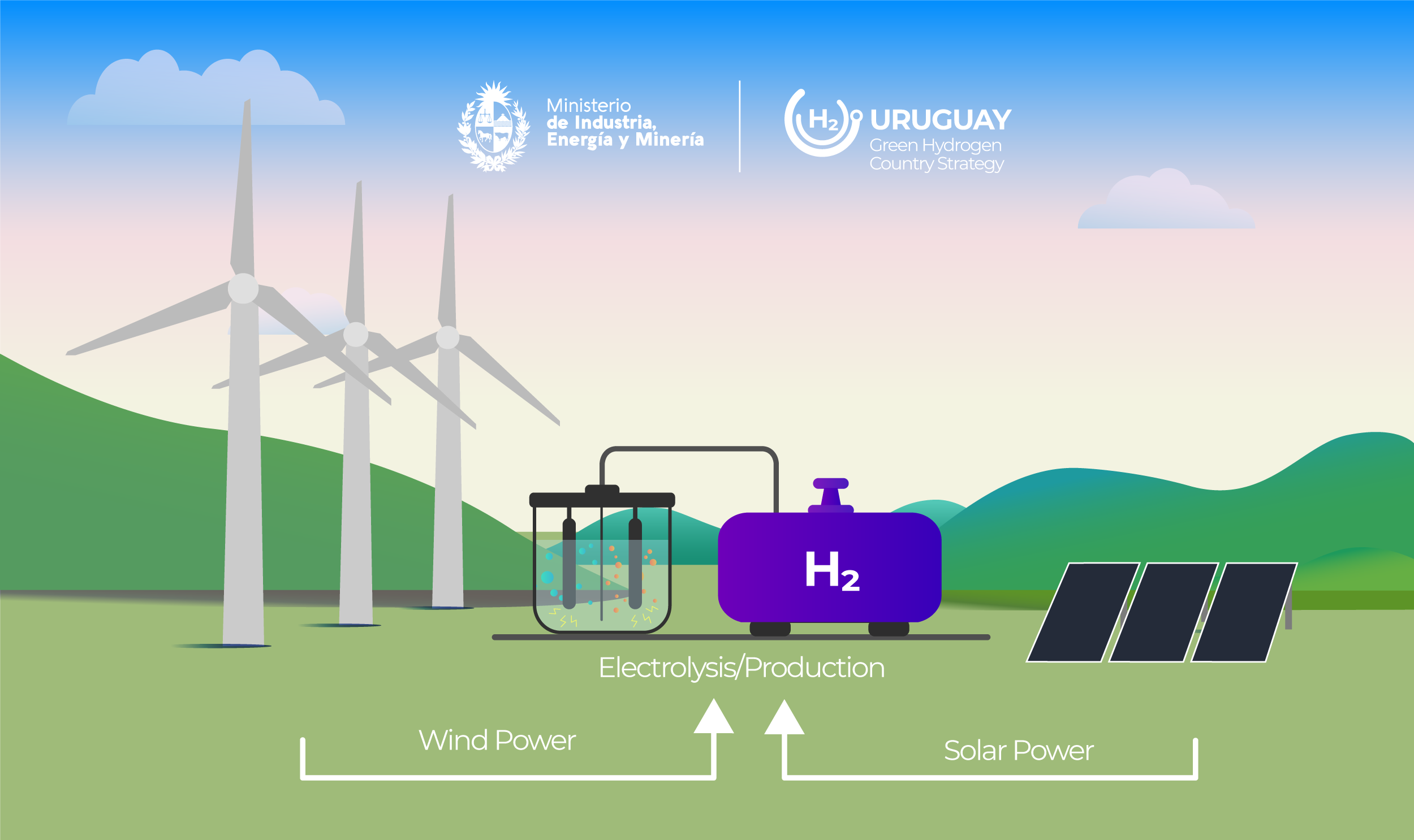
Currently the method with the greatest potential for the production of Green Hydrogen is from the electrolysis of water (H₂O), thus, from electrical energy from renewable sources and water (H₂O), it is obtained separately Hydrogen (H₂) and Oxygen (O₂). Therefore, the production of Green Hydrogen is a process with zero greenhouse gas emissions.
The use of Green Hydrogen is totally sustainable, since it is produced based on renewables and although water is used for the production of Green Hydrogen, after Hydrogen is used, the by-product is water vapour, with which the same amount of water returns to the environment and the cycle is closed. For example, if Hydrogen is used as energy in transport (consider for example a truck), the emission that will come out of the exhaust pipe will be water vapour (the same amount of water that was used to produce that Hydrogen).
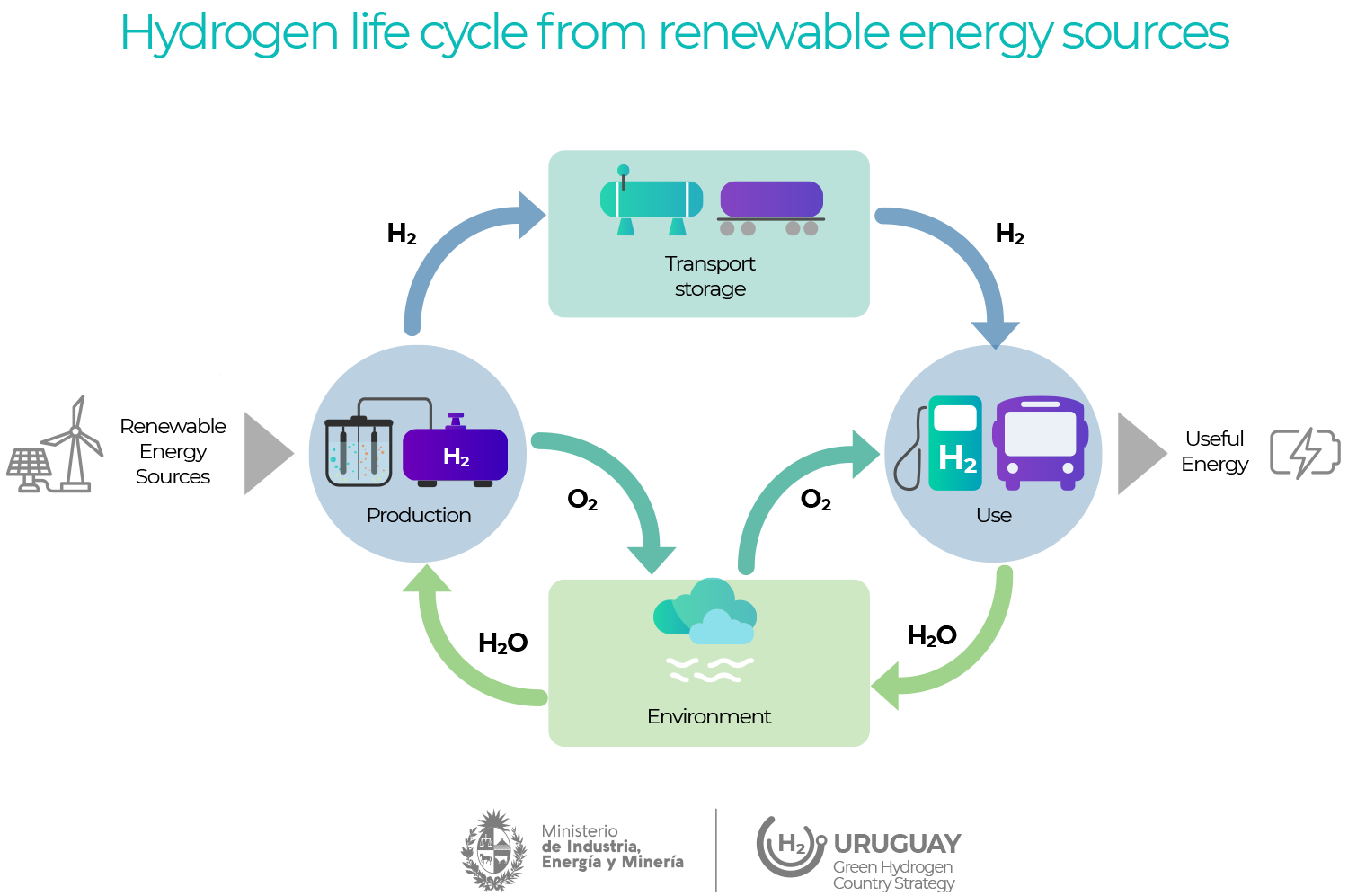
Source: ANCAP adaptation of C. Koroneos, A. Dompros, G. Roumbas, and N. Moussiopoulos, “Life cycle assessment of hydrogen fuel production processes,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, vol. 29, no. 14, pp. 1443–1450, 2004.
Why Green Hydrogen in the world and why now?
The commitment to Green Hydrogen is one of the axes of the second energy transition that our country is beginning to go through. According to the studies of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) of 2018, to limit global warming to less than 1,5ºC, carbon neutral must be achieved by the year 2050 at a global level.
Currently, energy consumption in the world is 80% from fossil fuels (REN21, 2019). Therefore, achieving global carbon neutrality by 2050 is a big challenge and it needs a very important energy transition.
In line with this, 120 countries have committed to having “zero” emissions by the year 2050 (unfccc.int). As a consequence, industries are making announcements along these lines. For example, the major brands in the automotive industry have announced that their vehicles will be zero emissions by 2050 and some of them even earlier (e.g.: General Motors in 2035). Other energy industries have also announced that they will be zero emissions by 2050, including companies which their main business is the sale of hydrocarbons such as: Shell, BP, etc.
Today, renewable energies are seen as the solution to generate energy that will later be used in all sectors of activity. In the long term, nuclear fusion could be developed to complement or replace renewables.
There is a worldwide consensus that Green Hydrogen (Hydrogen produced from renewable energies) will be key in the decarbonization of the energy sector and raw materials.
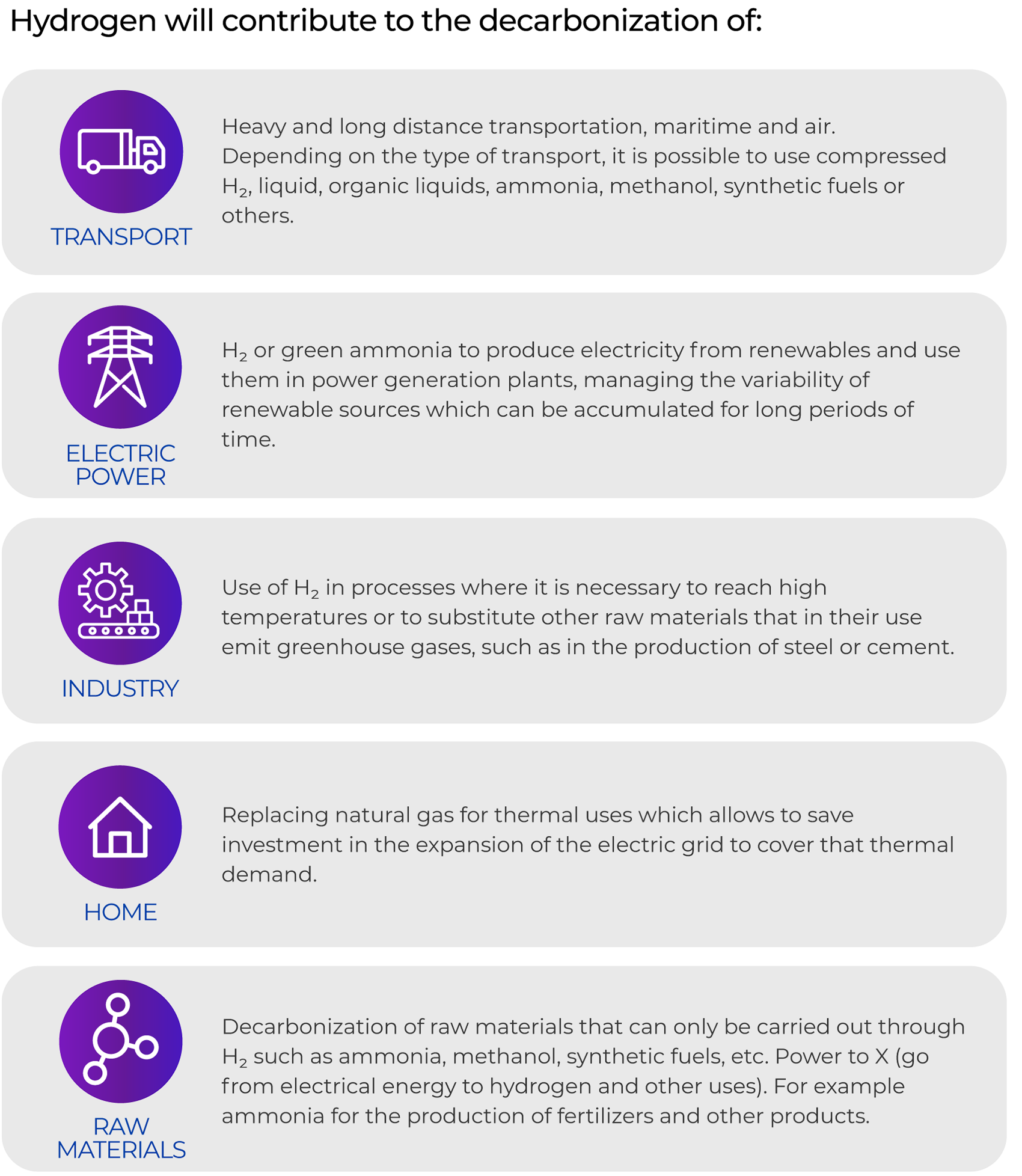
Ammonia is emerging to be one of the main forms of hydrogen transport for the export/import business between countries. In addition, it is expected to be one of the main alternatives to replace fossil fuels on ships.
Since 2020, after the beginning of the covid-19 pandemic, very important investments have been announced at the international level, both in the supply and in the demand of Hydrogen and its derivatives. The development of Green Hydrogen will change the geopolitics of the energy sector worldwide.
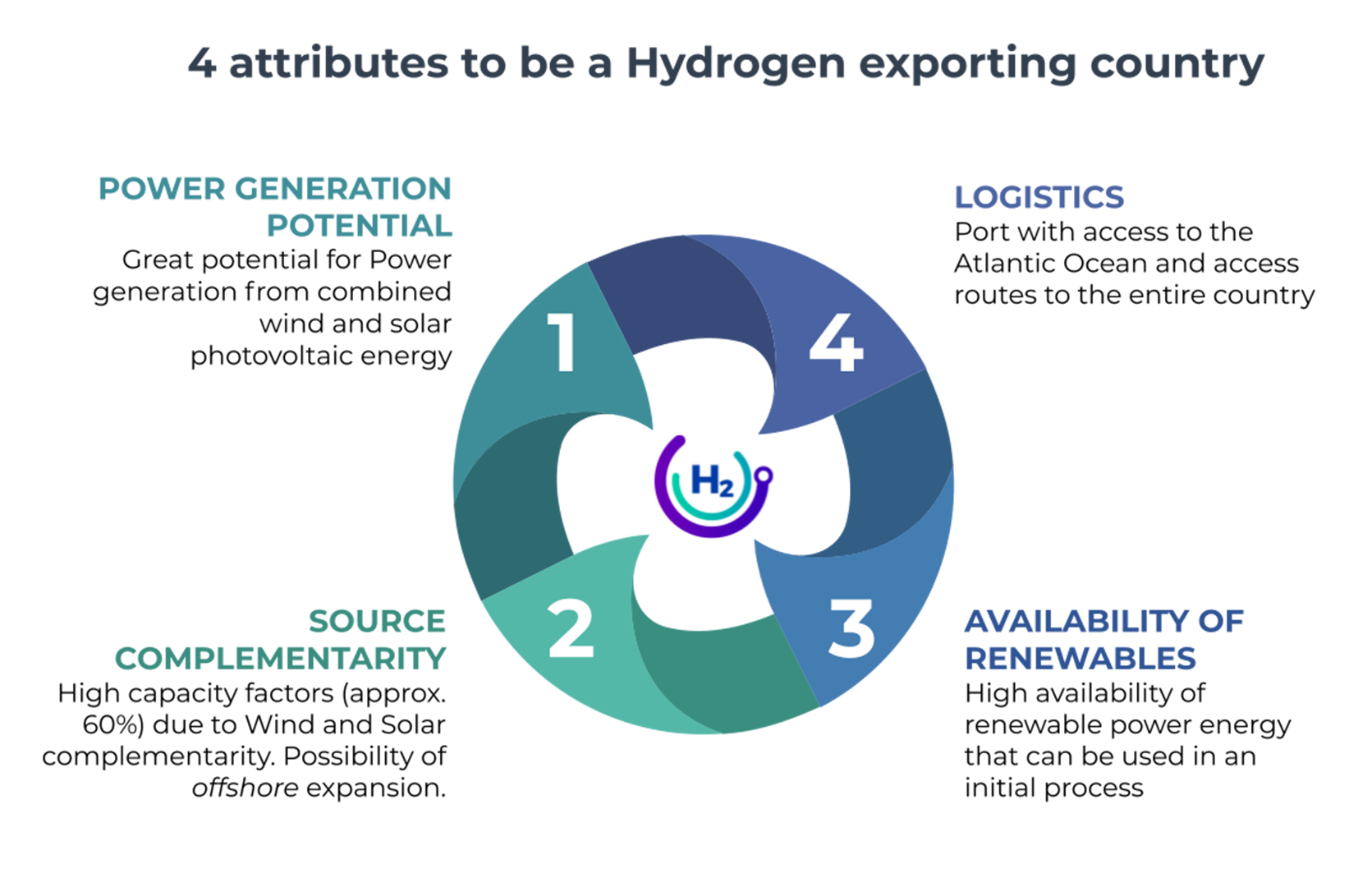
Why develop Green Hydrogen in Uruguay?
Uruguay is completing the first stage of its energy transformation from its almost total decarbonization of the electricity matrix. On average of the last 4 years (2017-2020), 97% of the electricity generated in Uruguay came from renewable energies (44% Hydro, 32% Wind, 18% Biomass, 3% Solar).
Why develop Green Hydrogen in Uruguay?
Uruguay is completing the first stage of its energy transformation from its almost total decarbonization of the electricity matrix. On average of the last 4 years (2017-2020), 97% of the electricity generated in Uruguay came from renewable energies (44% Hydro, 32% Wind, 18% Biomass, 3% Solar).
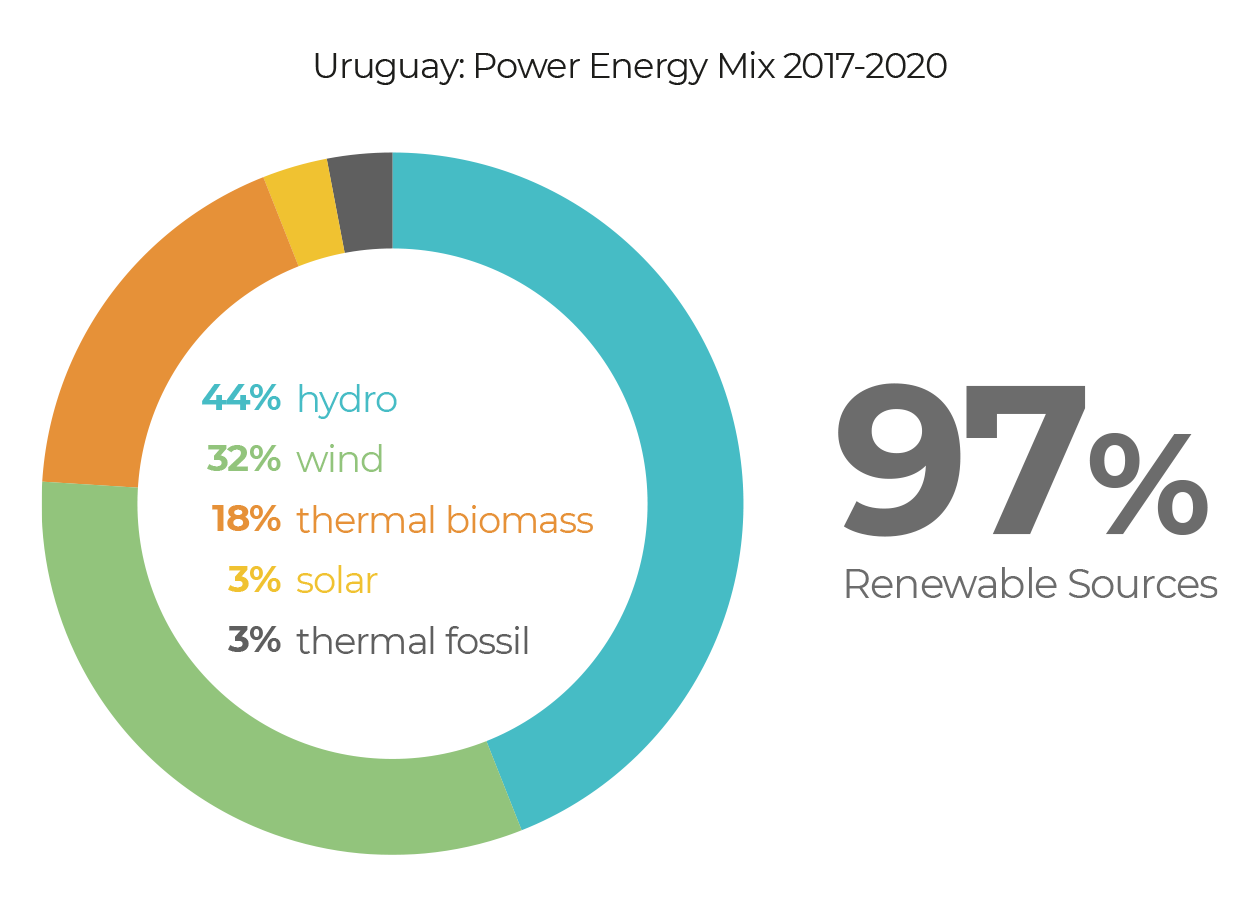
Source: BEN 2017, 2018, 2019 and preliminary 2020 (electric matrix)
The second stage of the energy transition in Uruguay includes various challenges, among which are the Development of a Hydrogen Economy and to continue with the decarbonization of the energy sector and the production of raw materials.
Regarding the Development of Hydrogen Economy, Uruguay has many attributes to be a producer of Green Hydrogen in order to: be exported, consumed locally directly and in industries related to the production of raw materials and green chemicals, which in turn can be consumed locally or exported.
To continue with the decarbonization of the energy sector, it is necessary to increase the share of renewables in the energy supply matrix, which is currently 63%, with the remaining 37% still of fossil origin (36% oil and 1% gas). Two thirds of this oil is used to supply the transportation sector.
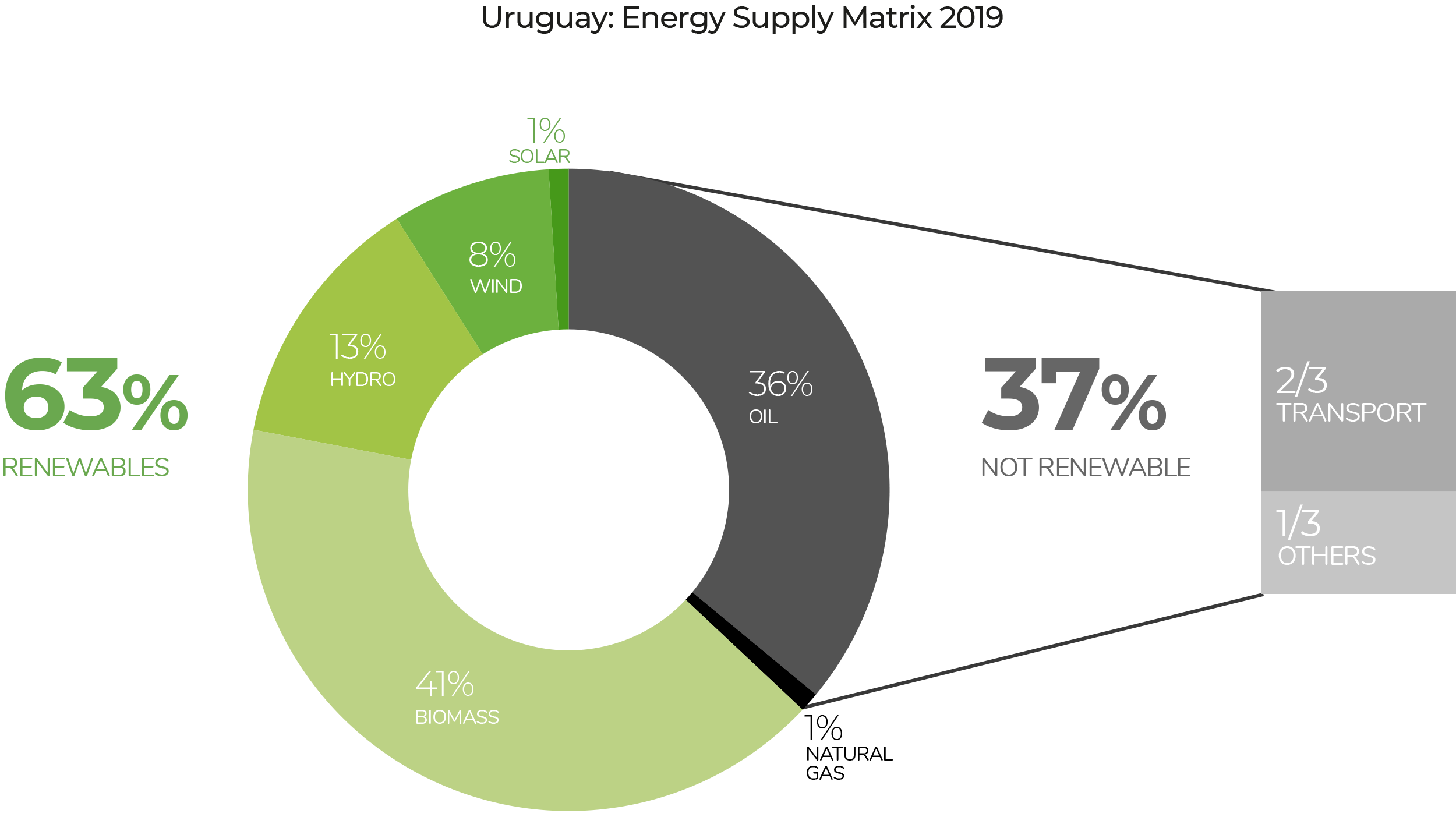
Source: BEN Primary sourcing matrix (year 2019)
Uruguay is interested in the decarbonization of raw materials and chemical products, both for domestic consumption and for export. There is particular interest in the production of green fertilizers since Uruguay and the region is an important center of agricultural production. It is also interesting to analyze the production of green steel, Uruguay has iron deposits that could be used. Also, it is of interest to Uruguay, the development of products such as ammonia, methanol, Green diesel (HVO), etc.
The incorporation of Green Hydrogen will give to Uruguay: industrial, economic and labor development, greater energy independence, reduced vulnerability to the volatility of oil prices and savings in foreign exchange.
